Article
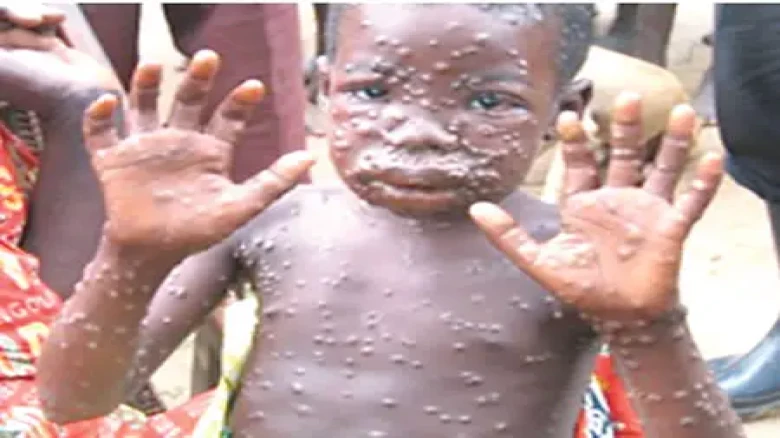
Squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, and a range of monkey species have all been reported to carry the monkeypox virus.
Digital Desk: Monkeypox is a zoonosis spreading from infected animals to people. According to the WHO, infections occur near tropical rainforests that are home to virus-carrying animals. Squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, and a range of monkey species have all been reported to carry the monkeypox virus.
The variola virus, which causes smallpox, and the vaccinia virus, used in the smallpox vaccine, are both members of the orthopoxvirus family. The symptoms of monkeypox are similar to those of smallpox; however, they are less severe.
Although smallpox was eradicated worldwide in 1980 due to vaccination, Monkeypox is still present in several countries in Central and West Africa and elsewhere.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO TRANSMIT HUMAN-TO-HUMAN?
Transmission between humans is prohibited. According to the WHO, the longest known chain of transmission is six generations long, which means the last person infected in this chain was six miles distant from the original sick person.
According to the WHO, transmission can occur through bodily fluids, skin lesions, internal mucosal surfaces like the mouth or throat, respiratory droplets, and infected objects.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF MONKEYPOX?
Smallpox symptoms are similar to those of monkeypox. They are, however, gentler. Symptoms of monkeypox include flu-like symptoms such as:
WHERE DOES MONKEYPOX DETECT FIRST?
In 1970, during increased efforts to eradicate smallpox, the first human case was detected in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
Human cases of monkeypox have been reported in 15 countries across four continents, according to the WHO.
Cases have been discovered in the United States, the United Kingdom, Israel, Singapore, South Sudan and Benin in Africa.
Leave A Comment