Regional
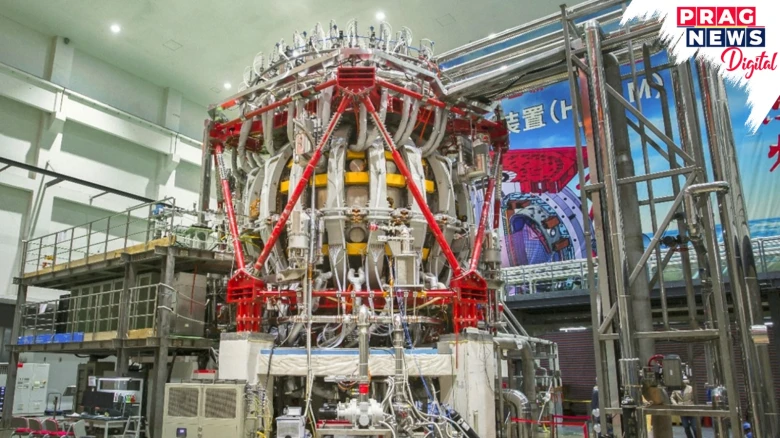
Digital Desk: China has achieved a remarkable milestone in nuclear fusion research with its Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), often referred to as the ‘artificial sun’. On 15th January 2025 EAST sustained plasma at a temperature exceeding 100 million degrees Celsius for a record time of 17 minutes and 46 seconds. This surpassed its previous record of maintaining plasma for 403 seconds in 2023.
EAST replicates the sun’s nuclear fusion process, where hydrogen nuclei combine to form helium, releasing vast amounts of energy. Achieving such extreme temperatures is crucial to initiate and maintain fusion reactions. Fusion produces minimal radioactive waste and relies on abundant fuel like hydrogen isotopes, making it a promising source of nearly limitless, clean energy.
This achievement is a significant step towards making nuclear fusion a practical energy source. It contributes valuable insights to the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) in France, which aims to demonstrate large-scale fusion power feasibility. Despite this progress, challenges remain, including developing materials that can endure extreme conditions and achieving continuous, self-sustaining reactions.
Fusion energy holds the potential to revolutionize energy generation, offering an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels. While practical fusion power plants are still years away, the success of EAST has brought the scientific community closer to realizing this vision.
China’s advancements highlight its leading role in the global race for fusion energy. As research continues, breakthroughs like this pave the way for a sustainable future powered by fusion, potentially addressing the world’s growing energy demands while combating climate change.
This landmark achievement underscores the transformative potential of fusion energy, making it a beacon of hope for a cleaner, greener future.
Leave A Comment