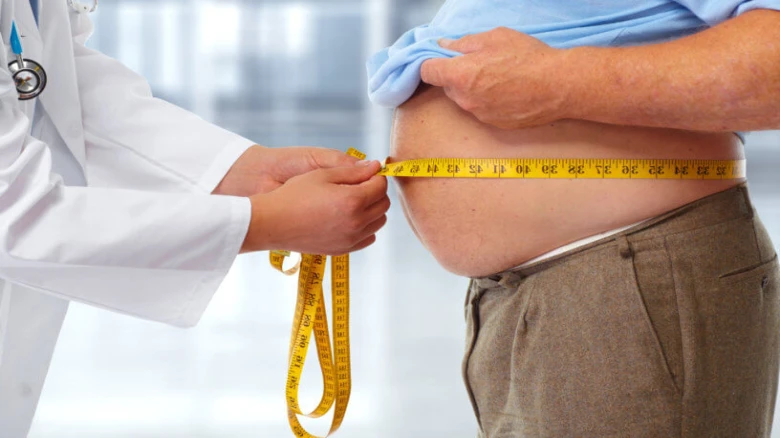
Obesity, which is characterized by dietary abundance, still raises many questions about the adaptation and interaction of cancer cells and immune cells in this altered nutritional milieu.
Digital
Desk: Obesity has become a global epidemic in recent years,
reaching frightening levels. Excess body mass index (BMI25kg/m2) not only has a
negative impact on overall health, but it is also firmly linked to an increased
vulnerability to a number of diseases. Among these is the well-established
relationship between obesity and cancer, with frequent updates from scientific
literature supporting the alarming association.
A
high BMI is an established risk factor for a variety of chronic diseases and
mortality, according to numerous research. However, the link between obesity
and some types of cancer has sparked widespread worry. Obesity is linked to a
variety of diseases, including esophageal (adenocarcinoma), colon, rectal,
kidney, pancreatic, gallbladder (in females), postmenopausal breast, ovarian,
and endometrial cancer.
While
nutrition has been demonstrated to enhance tumour growth, the key link between
obesity and these cancers is increased chronic inflammation and changes in
immune cell populations. Obesity, which is characterized by dietary abundance,
still raises many questions about the adaptation and interaction of cancer
cells and immune cells in this altered nutritional milieu.
Also Read :8 powerful physical and mental health benefits of hugging
In
2012, a large-scale global investigation shed light on the magnitude of the
problem. It was discovered that excess BMI in adults was responsible for around
3.6% of all malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer), or 13% of all
obesity-related cancers. This resulted in an estimated 481,000 additional
cancer cases in men and women in 2012 alone, which could have been caused by
obesity. Notably, postmenopausal breast, corpus uteri, and colon cancer
accounted for 73% of all attributable female cases, whereas kidney and colon
cancer accounted for 66% of all male-attributable cases.
It
is disturbing that 64% of all global cancer cases associated with excess BMI
were identified in Northern America and Europe, with South East Asia
contributing only 2%. According to recent figures, 35% of adults aged 20 and
over are overweight (BMI 25 kg/m2), with 12% categorized as obese (BMI 30
kg/m2). While the present incidence of excess BMI in many Asian and African
countries is approximately 10%, Pacific nations such as Cook Island and Nauru
record the greatest frequency, exceeding 90%, followed closely by other
affluent countries. Obesity in adults is currently predicted to be around 5% in
India, with the prevalence expected to quadruple by 2040. Worryingly, India's
prevalence of overweight and obesity is increasing faster than the global norm.
If we regard excess BMI to be a cause-and-effect relationship, the current pattern of population weight growth portrays a
bleak picture. Cancer's burden is expected to rise dramatically in the future
unless urgent action is made to prevent the obesity pandemic. The increased
understanding of the impact of obesity and food on the tumour microenvironment,
on the other hand, provides hope for the development of novel targets and
techniques to address the incidence, progression, and therapy of these
obesity-exacerbated malignancies.
In conclusion, the rise of obesity to epidemic proportions poses a grave threat to public health. The strong association between excess BMI and increased susceptibility to various diseases, particularly cancer, demands immediate attention. Governments, healthcare professionals, and individuals must join forces to tackle this pressing issue. Effective interventions, including public awareness campaigns, improved access to nutritious foods, and increased opportunities for physical activity, are crucial in curbing the obesity epidemic. By prioritizing prevention and adopting healthier lifestyles, we can potentially reverse the trajectory of this alarming trend and pave the way for a healthier future.
Source Credit: Dr Debashish Chaudhary